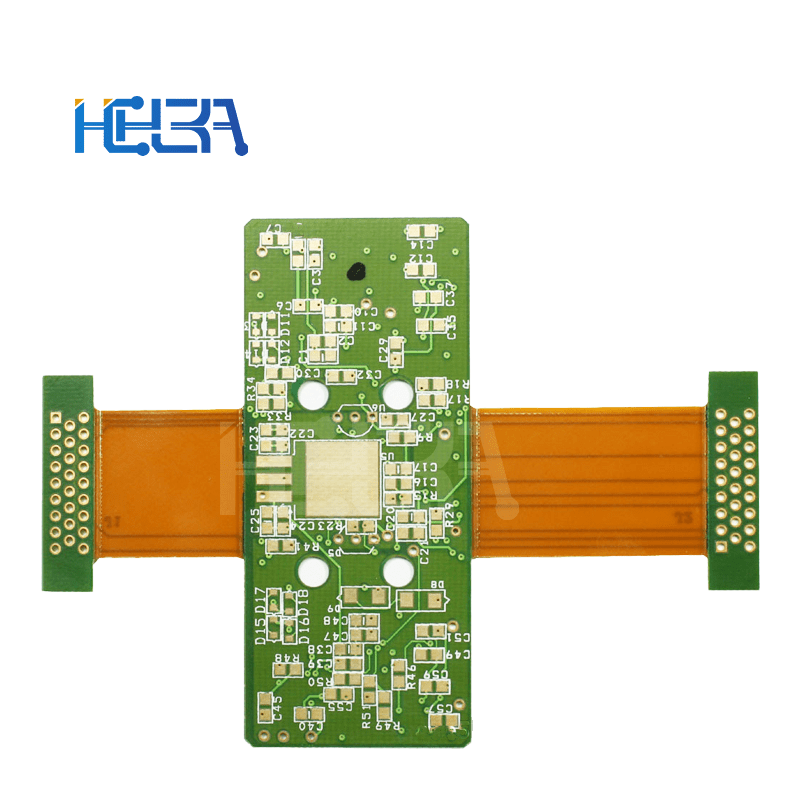
Description
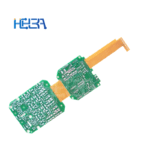
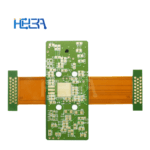
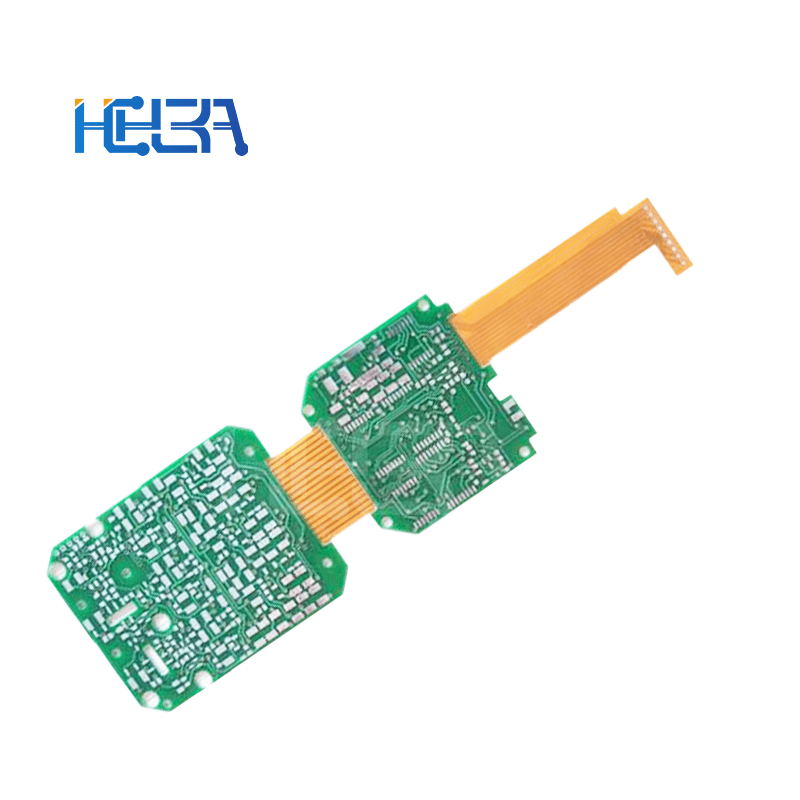
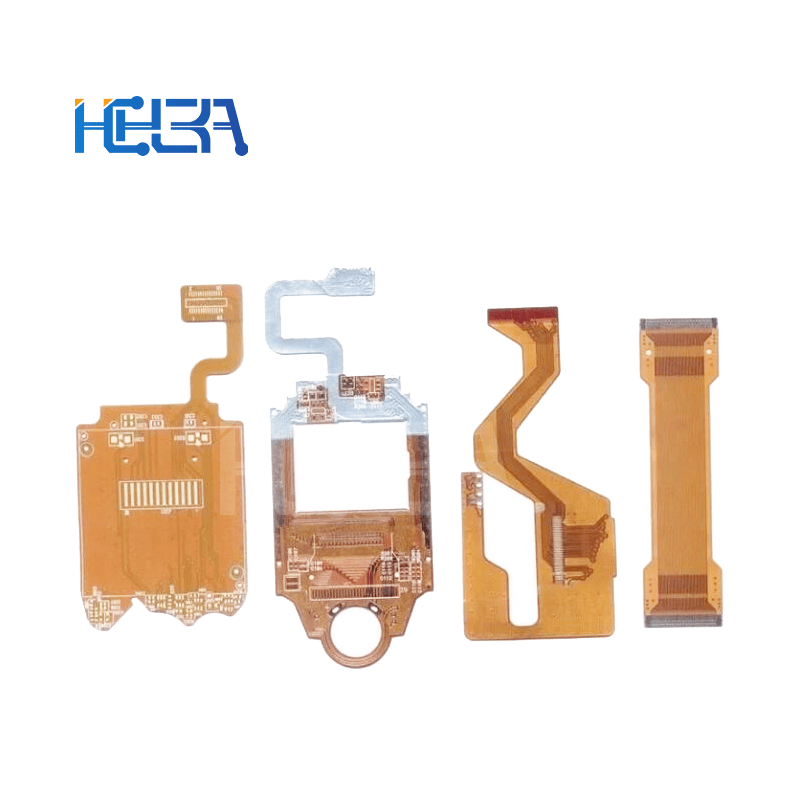
Flexible printed circuit board (FPCB) is a circuit board that combines a flexible printed circuit (FPC) and a rigid printed circuit board (PCB) through a certain process. It combines the flexibility of FPC and the stability and load-bearing capacity of PCB, and can meet the complex needs of some special electronic devices in spatial layout and function realization.
1.Structural characteristics
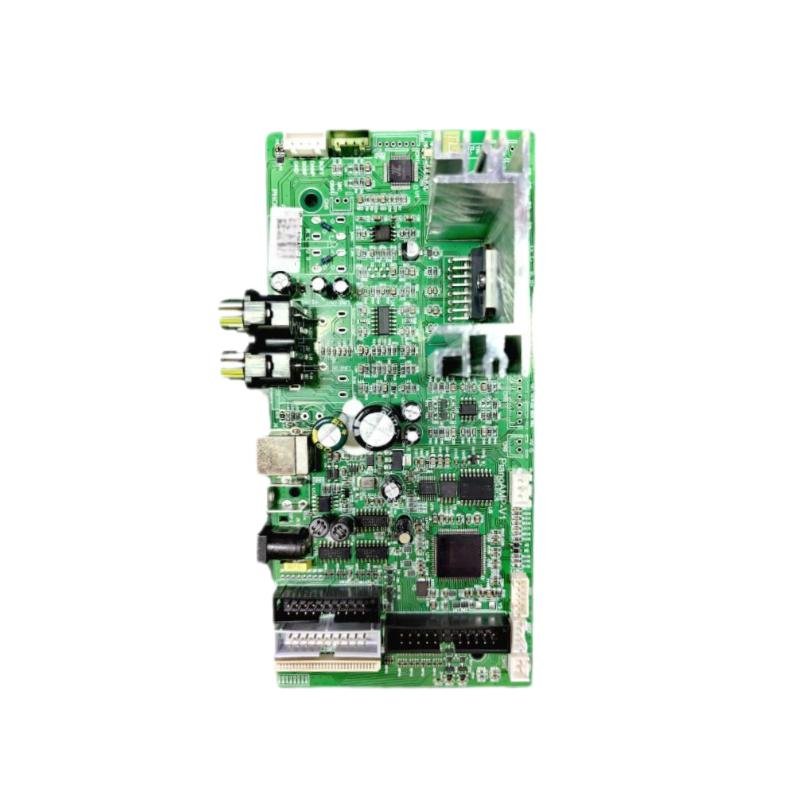
Layered structure: Generally composed of multiple layers of materials. From the most basic structure, it includes the outer circuit layer, the middle insulating layer and the via holes used to connect different layers. In the soft and hard combination part, flexible materials and rigid materials are closely combined. For example, in the motherboard design of a folding mobile phone, the flexible part can realize signal transmission to the folding area, and the rigid part is used to install large components such as chips.
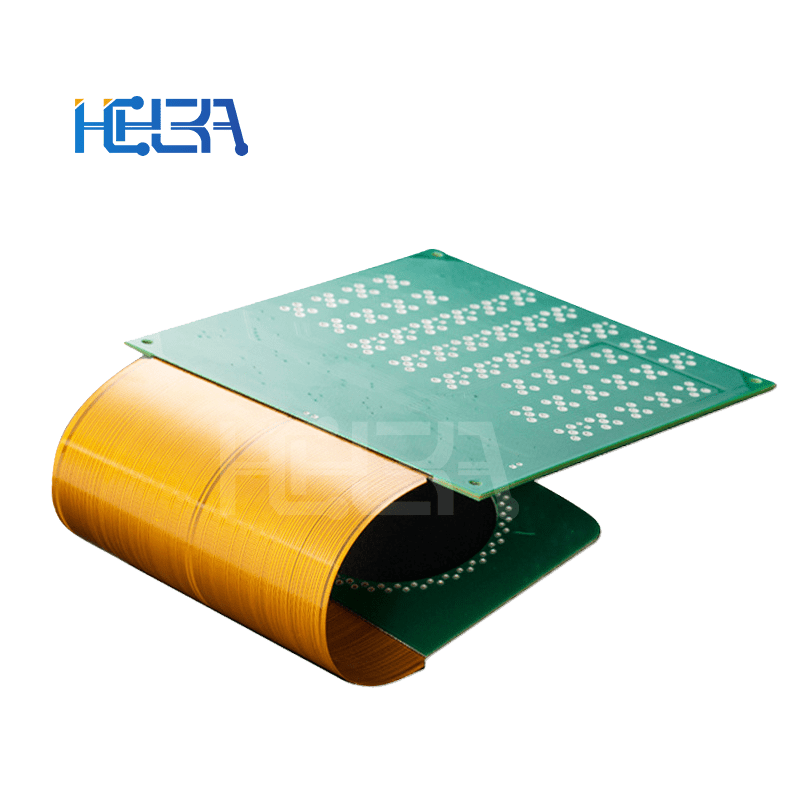
2.Manufacturing process
Preliminary preparation: First, design is carried out to determine the circuit layout, number of layers, and component positions of the soft and hard combined board. During the design process, factors such as signal integrity and electromagnetic compatibility need to be considered. Then, prepare materials, select appropriate flexible and rigid materials, and pretreat the materials, such as cleaning and drying, to ensure the cleanliness and good adhesion of the material surface.
Circuit fabrication:Pattern transfer: Transfer the designed circuit pattern to the copper foil through photolithography technology. In this process, photosensitive materials and exposure equipment are used to accurately copy the circuit pattern onto the surface of the copper foil to form the prototype of the circuit.
Etching process: Use chemical etching solution to etch away the copper foil not protected by the photosensitive material, leaving the required circuit pattern. The composition of the etching solution and the etching time need to be strictly controlled to ensure the accuracy and quality of the circuit.
Soft and hard combination process: This is a key step. Generally, lamination is used to combine flexible materials and rigid materials under high temperature and high pressure. In the lamination process, appropriate adhesives should be used, and parameters such as temperature, pressure and time should be controlled to ensure good bonding strength between the two materials.
Drilling and plating: Drilling is used to make vias to connect different circuit layers. Plating is to deposit a layer of metal (such as copper) on the hole wall to ensure the conductivity of the vias.
3.Application fields
Consumer electronics field: Widely used in smart phones, tablets, wearable devices, etc. Taking folding mobile phones as an example, the connecting lines in the folding part are realized through soft and hard combined boards, which can ensure the normal signal transmission and device operation of the mobile phone during folding and unfolding.
Automotive electronics field: It plays a role in automotive control systems, in-vehicle entertainment systems, etc. For example, the circuit board behind the dashboard of a car, partly using soft and hard combined boards can better adapt to the shape of the dashboard and ensure the signal transmission between various sensors and display modules.
Medical electronics field: Such as portable electrocardiogram instruments in medical monitoring equipment. Soft and hard combined boards can make the equipment more compact and lightweight, convenient for medical staff to carry and use, and can ensure the reliability of the equipment and the accuracy of signals in a complex medical environment.