How to Clean Electronic Circuit Boards: The Definitive Guide to Using a Printed Circuit Board Cleaner
Learn how to clean electronic circuit boards effectively using the right printed circuit board clean
What Are Electron Devices And Circuits? A Practical Guide by HCJMPCBA
Table of Contents
ToggleElectronic systems—ranging from industrial control panels to consumer gadgets—rely on electron devices and circuits to function. These systems combine electronic devices and circuit theory to control, process, and power everything we use today. In this guide, HCJMPCBA walks you through the definition, components, working principles, types, and sourcing best practices for electronic devices and circuits, helping OEM engineers, buyers, and decision-makers make informed choices.
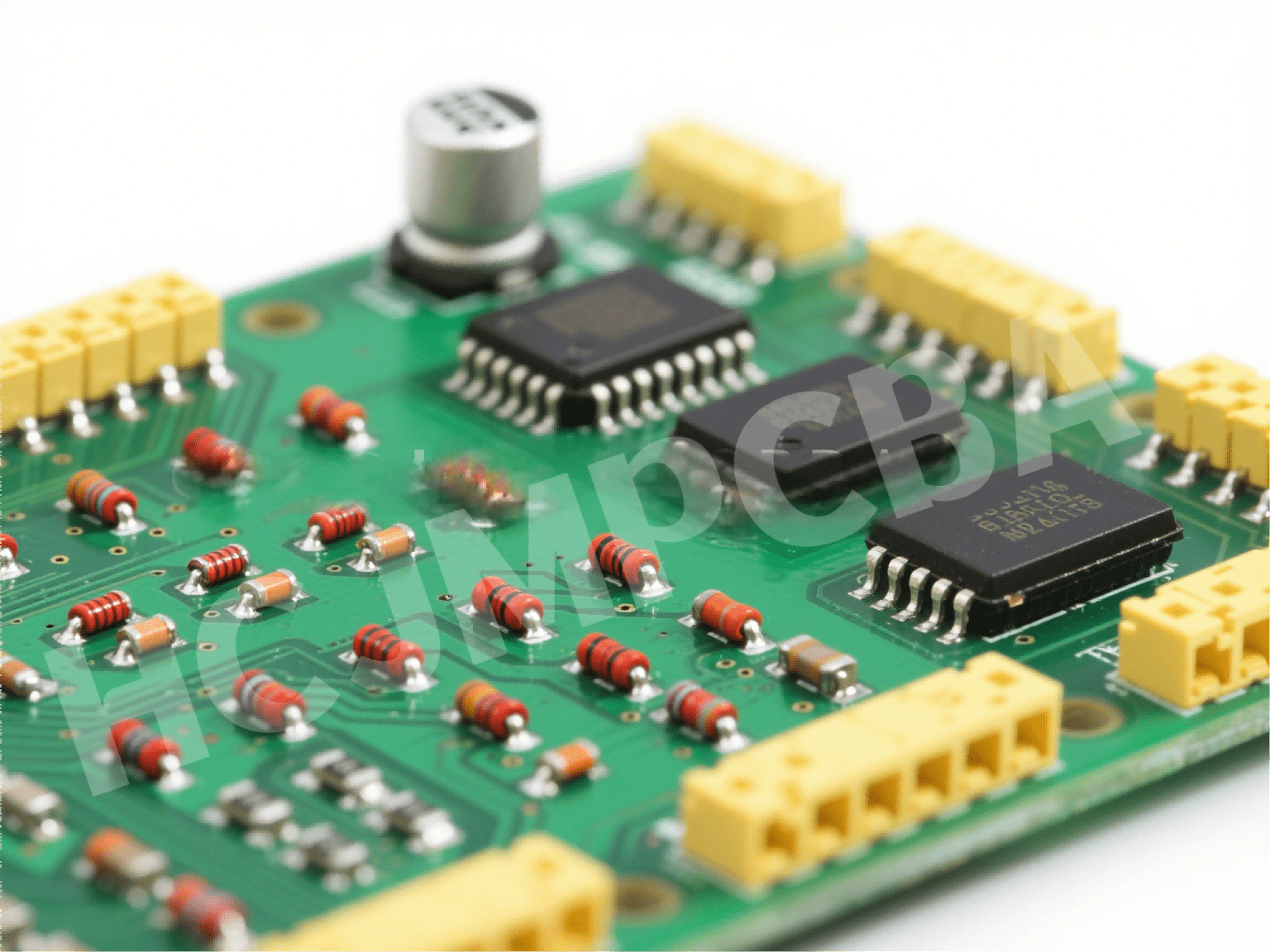
Electron devices and circuits refer to systems built with electronic components connected to form a working circuit. Electronic devices are the physical parts—like resistors, ICs, and sensors—while circuits combine them to perform tasks such as signal amplification, switching, or processing.
Key terms to know:
Electronic devices meaning, electronics devices definition
Components of electronic devices, electronic devices and circuit theory
According to industry guides, electronic devices are foundational building blocks in electronics systems, active or passive in nature.
Electronic devices fall into two categories:
Passive components (resistors, capacitors, inductors) — they manage currents but do not require power to operate.
Active components (transistors, ICs) — require power and can control or amplify signals. Integrated circuits pack multiple components into miniaturized forms.
Circuit boards host these components, linking them via copper traces to direct current and signals. When arranged correctly, they form circuits that:
Receive input signals or power
Process using active/passive components
Output actions (light, data, movement)
Key understanding of electronic circuit boards for sale, manufacturing of electronic devices, and surface mount devices is critical in modern PCBA manufacturing.
Electronic devices vary by function and integration:
Discrete components – single-function parts like LEDs or resistors
Modules or boards – assembled circuits like power modules or sensor arrays
Integrated Circuits (ICs) – compact chips with multiple circuit elements
Understand these types of electronic devices, kinds of electronic devices, and example electronic devices when planning your BOM or design.
Here’s a simplified breakdown to explain how electronic devices work within circuits:
Input Stage – Power or signal enters the board
Processing Stage – Active/passive components manipulate the signal (e.g., filter, amplify)
Output Stage – Signal drives action, such as motor movement or data output
Feedback/Control – Some systems read output and adjust parameters dynamically
Understanding electronic devices and circuit theory is vital in designing reliable We utilize this approach during PCBA validation to ensure consistent performance.
Grasping how electronics devices work ensures:
Proper component selection (e.g., SD-sized resistors vs SMD LEDs)
Optimized assembly techniques and board layout
Cost-effective sourcing without compromising reliability
Cleaner manufacturing and testing processes
Knowing surface mount devices, electronic devices types, and basic circuit theory allows better design-for-manufacturing and collaboration with suppliers.
Use these criteria to vet PCBA suppliers:
Device Knowledge and Handling – Can they assemble both passive and active components accurately?
Circuit Fabrication Capability – Support for multilayer boards and dense component placement?
Quality Assurance – Do they use AOI, ICT testing, and follow IPC standards?
DFM Support – Can they help optimize circuit layout for better performance and lower cost?
See our case studies to explore how we supported clients in optimizing circuit layouts.
Electron devices and circuits are made of components connected to perform useful functions.
Devices can be passive (resistors, capacitors) or active (transistors, ICs), often arranged into circuits via PCB traces.
Circuits receive inputs, process them through components, and deliver outputs or control signals.
Knowing this framework helps with better supplier selection and higher-quality PCBA outcomes.
By understanding how electronic devices work and leveraging the right components and circuits, professional teams ensure reliable and efficient electronics in every product.
Learn more about PCBA services, contact Guangzhou Huachuang Precision Technology.
Learn how to clean electronic circuit boards effectively using the right printed circuit board clean
Curious about the HDMI RF Modulator? Learn how HDMI RF modulators convert HDMI signals into RF for c
Automated Optical Inspection (aoi inspection pcb) is a non-contact, high-speed quality control metho