Description
HCJMPCBA specializes in state-of-the-art circuit board robot products built to meet the rigorous demands of robotics automation. Whether you need a robot circuit module with precise signal timing, protection against shorts (short circuit robot considerations), or advanced circuit robotics components for industrial, medical, or aerospace applications, HCJMPCBA’s PCB/PCBA assemblies deliver reliability, performance, and value.
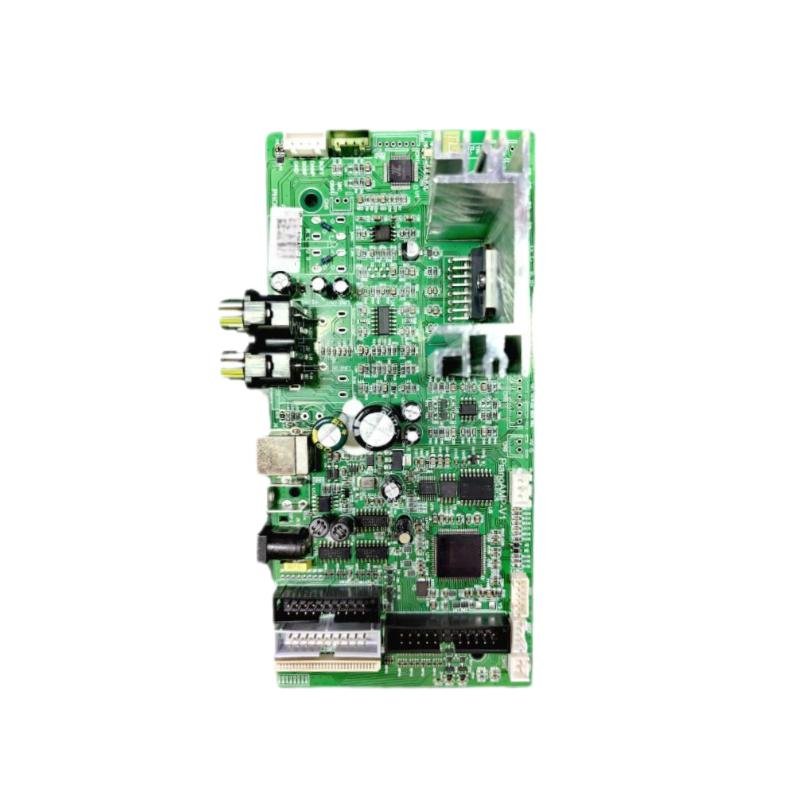
Professional Toy Accessories Custom Robot Circuit Board Electronic Pcba
Product Advantages / Technical Specifications
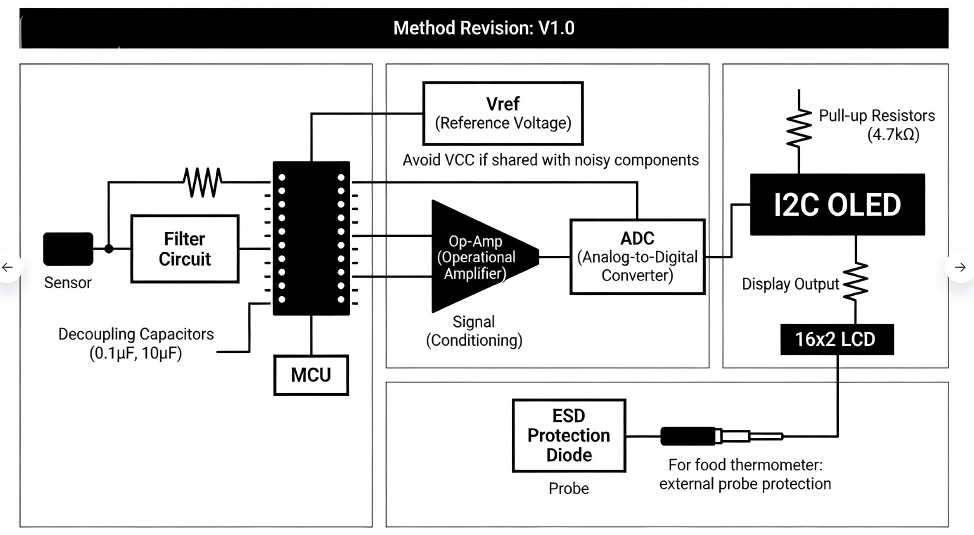
Here are the key technical parameters of our circuit board robot line, including how we design to prevent issues like short circuits, ensure robot circuit reliability, and deliver in challenging robotics environments.
| Parameter | Specification / Capability |
|---|---|
| Layers | 4 to 20 layers, including rigid, rigid-flex, flex designs |
| Minimum Trace / Space | Down to 3 mil / 3 mil on critical signal layers |
| Substrate Materials | High TG FR-4; Rogers / PTFE for high-frequency; Polyimide for flexible/rigid-flex boards |
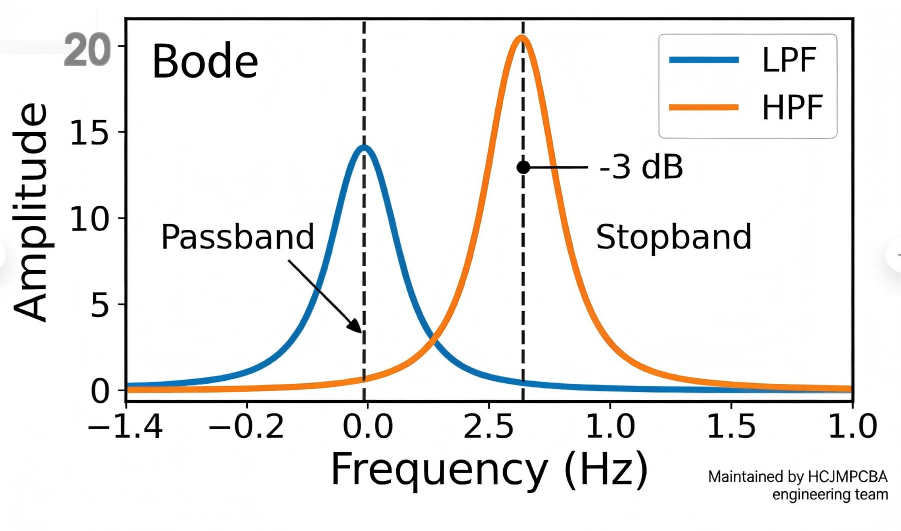
| Maximum Operating Frequency | Up to several GHz; controlled impedance specs within ±5% |
| Thermal Management | Heavy copper, thermal vias, heat spreaders, metal core options |
| Short-Circuit Protection & Safety | Conformal coating, fuse locations, overcurrent protection, clearance design |
| Environmental Reliability | Operating temp: -40°C to +85°C; humidity, shock, vibration resistant; certified RoHS / IPC Class III / CE / UL where required |
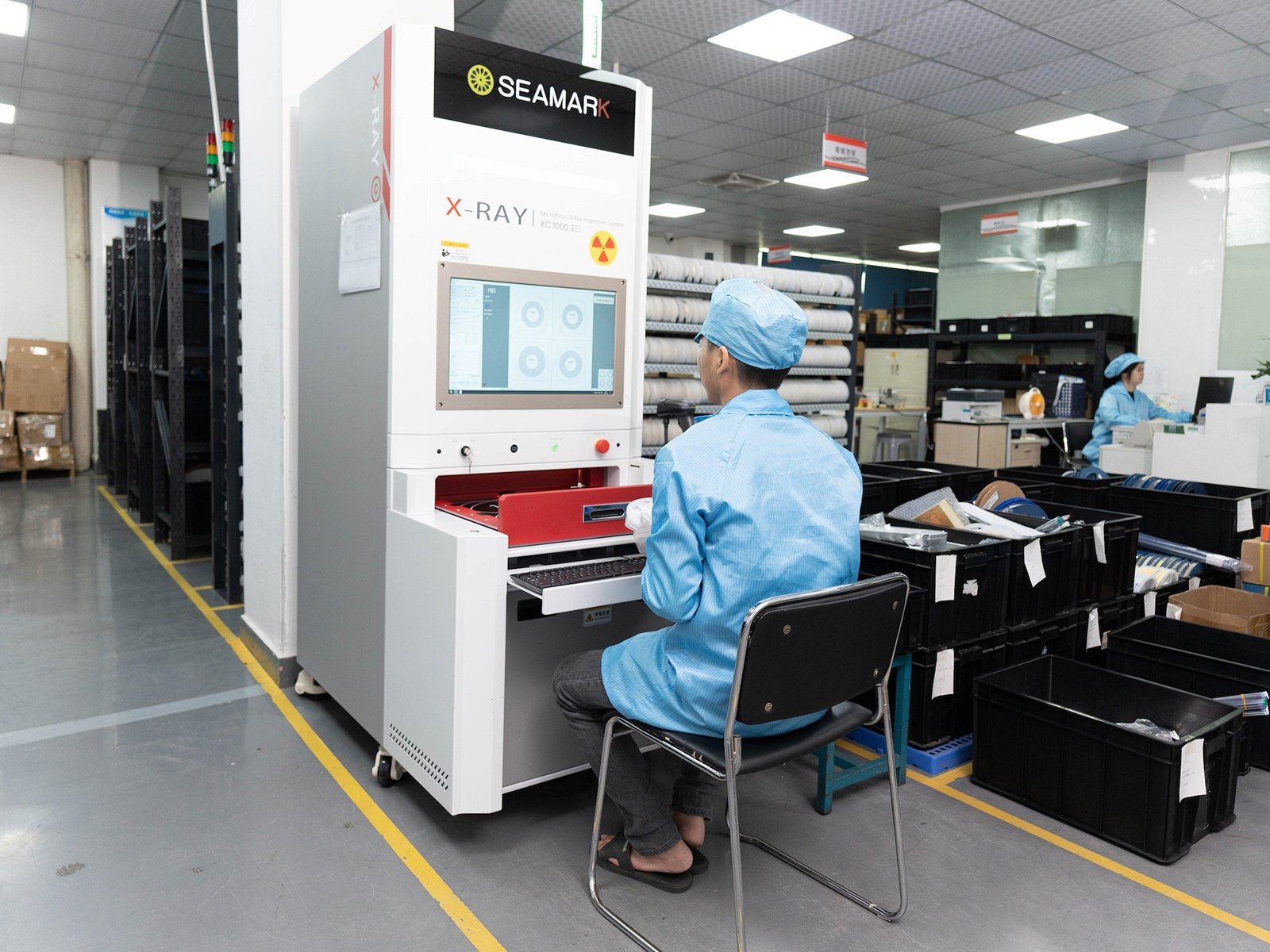
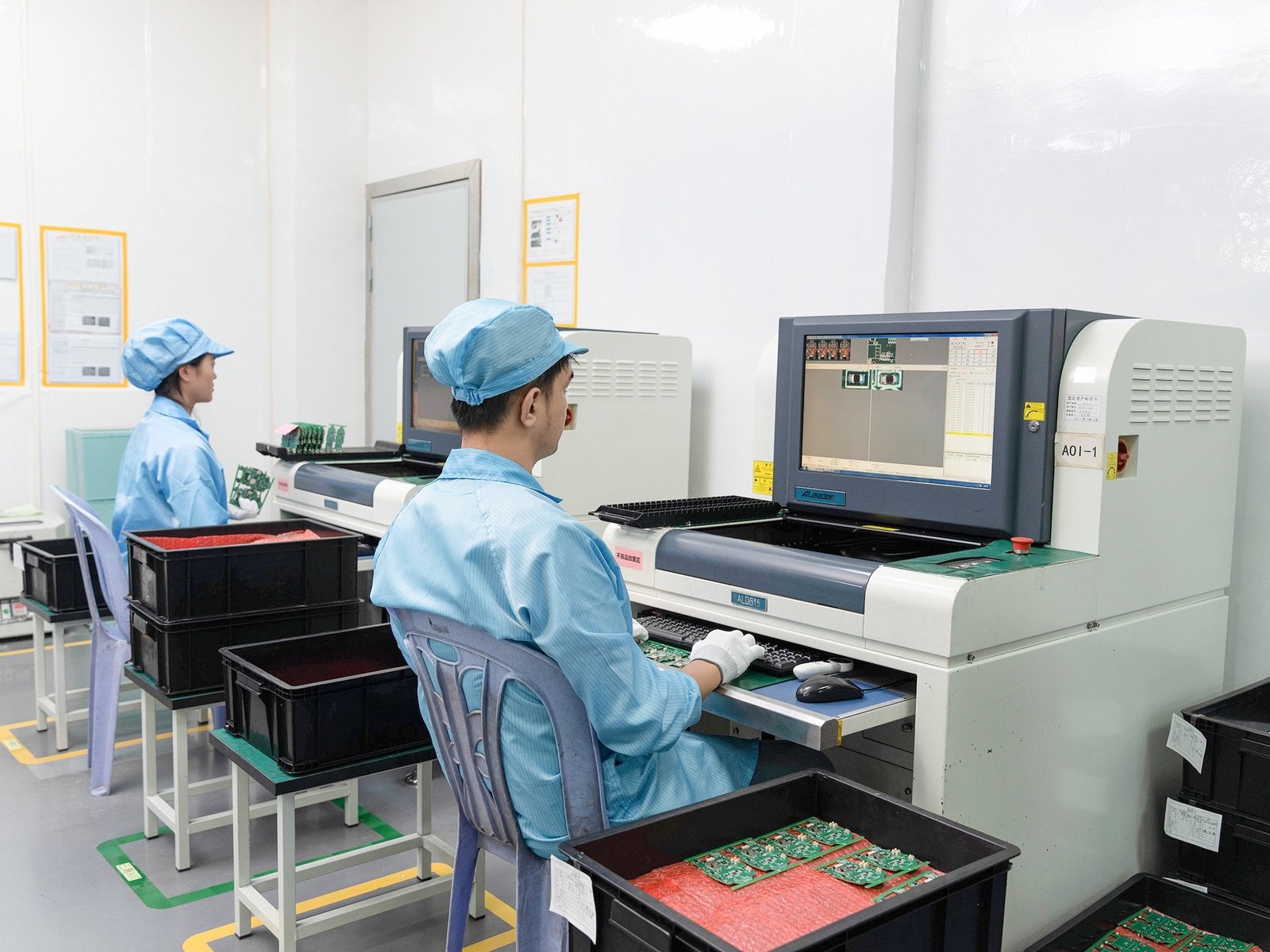
| Quality & Testing | 3D AOI, X-ray inspection, functional test, burn-in, power test, EMC/EMI compliance |
Use-Cases / Success Stories
Industrial Automation Robotics
A leading European automation OEM needed a robot circuit board that could handle high current motor drivers, frequent cycle braking, and tight thermal limits. Their previous boards suffered frequent failures, especially short circuit events during overload. HCJMPCBA engineered a 12-layer rigid-flex PCB with heavy copper + thermal vias and reinforced clearance margins. Result: failure rate dropped from 4.5% to < 0.5%, and service life increased 3× under duty cycle tests.
Medical Assistance Robots
A North American medical device company required a compact circuit robotics board for an assistive robot that operates near patients. They had issues with EMI interference and board overheating. HCJMPCBA redesigned the layout: optimized ground planes, matched trace widths, rigid-flex substrate for compact form, improved isolation. The final design passed strict EMC / CE testing and reduced temperature rise by 35%.
Research & Educational Robots
An R&D lab building a “short circuit robot” demonstration (educational use) needed boards with clear short protection (to avoid student mishaps) plus low cost for prototypes. HCJMPCBA delivered prototype boards (4-layer, FR-4) with protective fuses, silk-screen short warnings, and low MOQ. The prototypes were delivered in 12 working days, with excellent signal integrity for the motion control circuits.
Why Choose HCJMPCBA?
HCJMPCBA stands out in robotics PCB / PCBA OEM supply because:
Decades of PCB / PCBA Experience & Certifications: ISO 9001, IPC Class III, UL / CE compliance – proven track record in robotics, industrial, medical fields.
Design for Reliability: Early DFM / DFT reviews: prevention of short circuits, rigorous signal integrity design, controlled impedance.
Superior Testing & QC: 3D Automated Optical Inspection, X-ray, EMI / EMC testing, environmental stress (vibration, thermal cycling) for robot circuit boards that operate in demanding conditions.
Fast Prototyping + Scalable Production: Prototype boards in 10-15 working days; volume production scaled up with consistent quality and delivery.
Material & Manufacturing Flexibility: Rigid, flex, rigid-flex; FR-4, Rogers / PTFE, metal core; specialized finishes; ability to adapt to customer needs for robot circuit modules.
Common Questions (FAQ)
What is a “circuit board robot”?
A board designed specifically for robotics systems: control, power regulation, signal interfaces, often including protections for short circuits and thermal stress.How does HCJMPCBA handle “short circuit robot” protection?
By using design practices – sufficient spacing, overcurrent protection, fuses, protective coatings, thermal management – to minimize risk of shorts and damage.What lead time and minimum order quantity (MOQ)?
Typical prototype orders: 10-15 working days; volume orders vary depending on complexity, layer count, materials. MOQ is low for prototypes; higher for custom rigid-flex / high layer count boards.
Request a Quote
Want to bring your robotics project to life with a high-quality circuit board robot? Request a Quote today from HCJMPCBA and get prototyping, sample, or mass-production pricing.
Explore our detailed case studies to see real engineering outcomes and how HCJMPCBA solves intricate robot circuit challenges.