7 Essential Steps to Flawless PCB Assembly: Mastering Circuit Board Soldering with Precision
Learn pcb assembly best practices with our in‐depth guide on soldering circuit boards. Explore adv
12 Critical Insights into Series Circuits: The Industrial Engineer’s Guide to High-Reliability PCBA Manufacturing
Table of Contents
ToggleA series circuit is an electrical configuration where components are arranged in a single, continuous path, allowing the same current to flow through every element sequentially. This guide is maintained by the HCJMPCBA engineering team and updated with production checklists to ensure theoretical designs translate into high-yield, traceable PCBA reality.
Single Path Integrity: In a series circuit, there is only one path for electrons; a break at any point (like a cracked solder joint) stops the entire system.
Constant Current: The current in a series circuit remains identical at every point, making it ideal for LED arrays but sensitive to resistance fluctuations.
Industrial Traceability: For mission-critical series arrays, traceability (lot/batch/serial) is the only way to guarantee that a single component failure doesn’t compromise the entire production run.
| Feature | Series Circuit | Parallel Circuit |
| Circuit Series Definition | Components in a single loop | Components in multiple branches |
| Voltage Distribution | Shared: V_{total} = V_1 + V_2 + … | Equal: V_{total} = V_1 = V_2 |
| Current Behavior | In a series circuit the current is constant | Divided across branches |
| Failure Impact | One failure breaks the whole loop | Other branches remain functional |
| Best For | Voltage dividers, LED strings, Sensors | Household wiring, Power distribution |
To truly define series circuit logic in a manufacturing context, we must look beyond the textbook. While a series circuit definition in physics focuses on the sequential flow of electrons, in PCBA, a series circuit represents a reliability chain.
A simple series circuit consists of a voltage source and at least two components connected end-to-end. When you define a series circuit, you are essentially describing a system where the total resistance is the sum of all individual resistances. This leads to the fundamental rules of a series circuit: if the resistance of one component increases (due to aging or poor soldering), the current in series circuit flow decreases for the entire system.
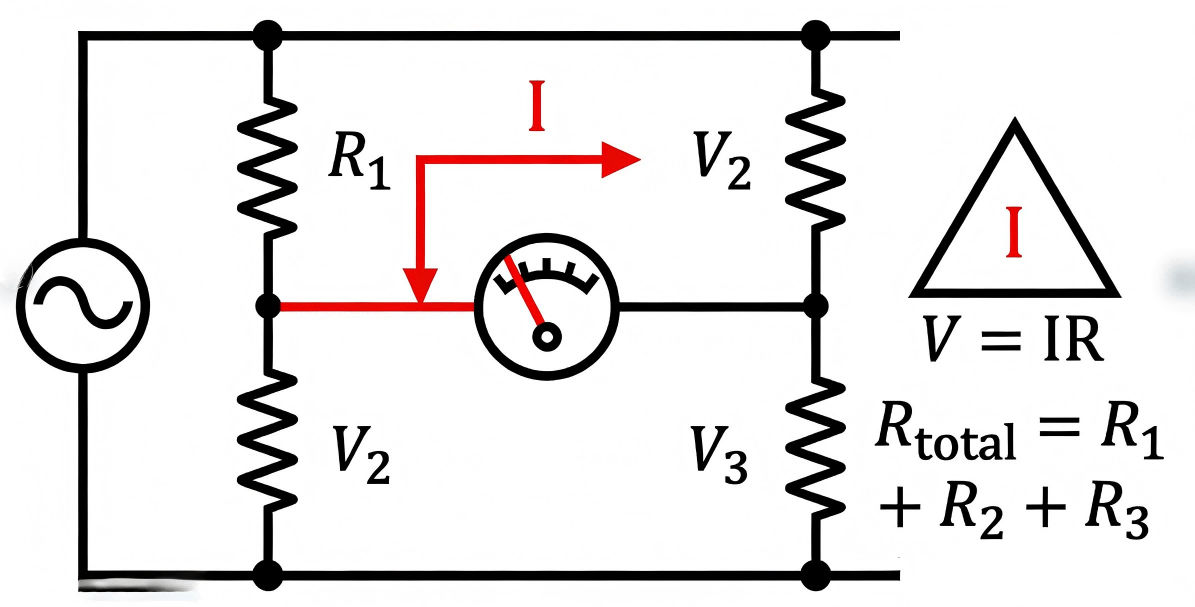
The Definition Of Series Circuit In Industrial
For engineers and technicians, knowing how to find current in series circuit configurations is the first step in thermal management.

Step By Step How To Find Current In A Series Circuit
The characteristics of a series circuit make it both useful and vulnerable. Because what happens to voltage in a series circuit is a cumulative drop across all loads, a single poorly manufactured resistor can cause the “downstream” components to receive insufficient voltage.
What is an advantage of series circuits? They allow for simpler wiring and are excellent for current-sensing applications. However, the benefits of a series circuit are lost if the PCBA process lacks traceability (lot/batch/serial). If a series of resistors is from a faulty batch, the entire circuit series will underperform.
At HCJMPCBA, we don’t just assemble boards; we de-risk your design. When you submit a series circuit design, we apply our proprietary reliability protocols.
Every PCBA project is assigned a unique Method Number + Revision. This ensures that the specific soldering temperature, flux chemistry, and pick-and-place speed for your series circuit simple design are locked in. If a revision is made to improve the yield, it is documented and traceable.
In a circuit series definition, every component is a critical link. We utilize a full traceability (lot/batch/serial) system. We can track exactly which lot of capacitors was used on a specific serial numbered board. If a component fails in the field, we can identify exactly which other boards in the batch are at risk.
We don’t guess; we test. Our sample plan follows ISO 2859-1 standards. We define strict test conditions (ambient temperature, input voltage, load) to ensure the voltage in a series circuit remains within your specified tolerances under real-world stress.
We provide our clients with the raw data from our automated testing stations. This includes the actual measured current in series circuit for every board, not just a “Pass/Fail” sticker.
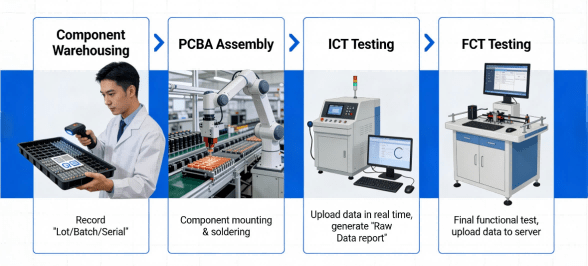
Hcjmpcba Manufacturing Standard For Series Circuits
| Engineering Requirement | Verification Method | Evidence Provided to Client |
| Current Stability | 100% Functional Test (FCT) | Raw Data (Amps/mAmps) |
| Voltage Integrity | Precise Test Conditions | Voltage Drop Analysis Report |
| Component Reliability | Traceability (Lot/Batch/Serial) | Component Source Certificate |
| Process Consistency | Method Number + Revision | Manufacturing Process Log |
| Thermal Performance | Thermal Imaging (Sample Plan) | Heat Dissipation Map |
To ensure your PCBA supplier meets the standards described in this definition of a series circuit guide, include this in your RFQ:
“Supplier must provide full traceability (lot/batch/serial) for all active and passive components. Manufacturing must be governed by a unique Method Number + Revision system. Final inspection must include raw data reports for all test conditions defined in the functional test specification.”
1.Inadequate Trace Width: Failing to realize that the current in series circuit is constant, meaning the trace must be rated for the maximum load for the entire length.
2.Ignoring Voltage Drop: Not calculating how to find voltage in a series circuit correctly, resulting in the last component in the chain having insufficient power.
3.Thermal Overload: Placing high-resistance series components too close together, creating “hot spots.”
4.No Bypass Protection: Designing a simple series circuit without a Zener diode or bypass path, leading to total system failure if one component fails.
5.Poor Batch Control: Using mixed lots of resistors with varying tolerances, leading to unpredictable voltage in a series circuit across different boards in the same batch.
Q: What is a series of circuit pitfalls in high-voltage designs? A: In high-voltage series circuits, the cumulative voltage can exceed the insulation rating of the PCB material (FR4). At HCJMPCBA, we use test conditions that include Hi-Pot testing to ensure safety.
Q: How does a series circuit work in LED backlighting? A: LEDs are often placed in series to ensure they all receive the exact same current, resulting in uniform brightness. We use raw data from our FCT to ensure every LED string meets the exact lumen/current requirements.
Q: What happens to the voltage in a series circuit if the load increases? A: If the total resistance increases, the current in series circuit decreases (if the source voltage is constant). This is why calculating how to find the voltage in a series circuit for each component is vital for sensitive ICs.
Q: What is a series circuit definition in the context of battery packs? A: It is the stacking of cells to increase voltage. We apply strict traceability (lot/batch/serial) to battery PCBA to ensure every cell comes from the same manufacturing batch for balanced charging.
Q: Whats a series circuit’s biggest weakness in harsh environments? A: Vibration. Since a series circuit has one path, a single cracked solder joint from vibration kills the device. Our Method Number includes specific soldering profiles to maximize joint strength.
When you partner with us, you don’t just get a board; you get a certified link in your supply chain. You can request:
The Method Number + Revision history for your specific project.
The Sample Plan results for your latest production run.
Complete traceability (lot/batch/serial) logs for every critical component.
Raw data from our automated test equipment (ATE) showing the exact voltage in a series circuit measurements.
Whether you are designing a simple series circuit for a consumer toy or a complex circuit series for an industrial sensor, the physics remain the same. However, the manufacturing execution makes all the difference. By focusing on traceability (lot/batch/serial) and rigorous test conditions, HCJMPCBA ensures that your “series circuit definition” becomes a reliable, market-ready product.
Update triggers: standard revision changes / recurring questions / production checklist updates.
Learn pcb assembly best practices with our in‐depth guide on soldering circuit boards. Explore adv
Guangzhou Huachuang Precision Technology specializes in high-reliability BGA assembly, offering prec
Looking for a professional digital thermometer circuit diagram or a precise thermometer drawing for