Revolutionizing Electronics with Advanced PCB & PCBA Solutions
This article provides a comprehensive overview of PCB and PCBA, their significance, manufacturing pr
How to Discharge a Capacitor Safely: A Complete Guide for PCB/PCBA Professionals
Table of Contents
ToggleIn PCB/PCBA environments, knowing how to discharge a capacitor is critical. Engineers and procurement professionals understand that capacitors discharging improperly can lead to equipment damage, downtime, or even serious injury. This guide unveils multiple safe, tested methods—enabling professionals to discharge safely and avoid the dreaded “death by capacitor” scenario.
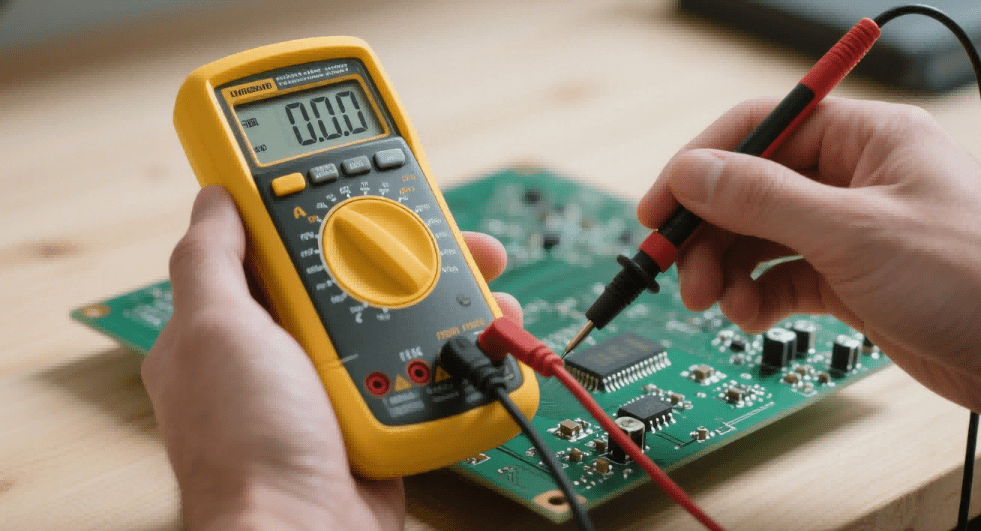
A capacitor stores electrical energy and may retain a dangerous charge even after power removal. In PCBA contexts, such residual voltage can harm technicians and tools unless fully discharged. Whether dealing with electrolytic, ceramic, or film capacitors, understanding capacitor discharge behaviour is foundational to safety and efficiency.
Capacitors, particularly large or high-voltage types, pose risks including electric shock, sparks, and equipment damage. Always disconnect the power supply first, wear insulating PPE, and use appropriate tools. Avoid direct shorting unless absolutely necessary, as this may cause arcing or PCB damage.
A bleeder resistor connects across the capacitor’s terminals, slowly and safely bleeding the charge. It’s a standard, cost-effective solution, often built into power supplies for passive discharge. 维基百科
Steps (professional tone):
Power off and verify isolation.
Select resistor (balance between discharge rate and minimal idle drain).
Connect across terminals.
Wait ~5×RC.
Confirm discharge via multimeter.
Use only for low voltage (<50 V). Touch both terminals with an insulated screwdriver to short and quickly discharge. Risky due to sparks, but can serve as “emergency use only.”
A light bulb acts as a visual resistor: it dims as the capacitor discharges. It’s safe, visible, and gentle on components.
These tools often have built-in resistors or controlled circuits, designed for larger or hazardous capacitors. They ensure controlled discharge with minimal risk.
The safest and most controlled approach:
Use a 5 kΩ–20 kΩ resistor, ≥5 W rating.
Measure initial voltage with a multimeter (DC mode).
Connect resistor via insulated clips.
Wait (20–60 s depending on capacitance.)
Confirm near-zero volts; repeat if needed.
RC time-constant (τ = R×C) dictates discharge duration. After ~5τ, voltage drops effectively to zero. For example, a 10 µF cap with 1 kΩ resistor discharges to 0V in ~0.05 s.
Ensure resistor power rating withstands P = V²/R.
Capacitors can self-recharge due to dielectric absorption even after discharge. A permanent bleeder resistor helps mitigate this.
Bleeder resistors rated for your system’s voltage.
Insulated tools (screwdrivers, clips).
High-voltage rated multimeter.
Dedicated discharge probes or pens.
PPE (insulating gloves, eye protection).
– Implement lock-out/tag-out SOPs and designated discharge areas.
Q: What to do before discharging?
F: Verify power off, assess voltage, select tools and PPE.
A: Disconnect, measure, discharge safely, verify, repeat if needed, store or tag.
How do I discharge a capacitor safely? Use resistor + multimeter or dedicated tool.
How long do capacitors hold charge? Hours or days—always verify.
Can I just unplug and wait? No—dielectric absorption & slow discharge can leave residual charge.
What resistor value should I choose? Typically 1 kΩ–20 kΩ, wattage rating should exceed expected energy.
Is shorting with a screwdriver safe? Only for low-voltage, emergency use—and with proper insulation.
Reddit insight:
“If the meter shows any voltage, discharge the cap with a resistor that will handle the heat … use a resistor with more ohms to reduce current flow.”
Understanding how to discharge a capacitor is foundational for safety and reliability in PCBA and PCB assembly. Whether employing a bleeder resistor, insulated tool, light bulb, or resistor + multimeter method, the goal remains the same: controlled, verified discharge with minimal risk.
To integrate these practices into your PCBA operations or if you’d like to learn more about HCJMPCBA’s PCB/PCBA services, please contact Guangzhou Huachuang Precision Technology.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of PCB and PCBA, their significance, manufacturing pr
Learn 5 powerful customer communication strategies that position HCJMPCBA as one of the best PCB man
This article analyzes the future trends of the electronic manufacturing industry, including technolo