Revolutionizing Electronics with Advanced PCB & PCBA Solutions
This article provides a comprehensive overview of PCB and PCBA, their significance, manufacturing pr
What Are Electronic Devices and Circuits—and How Do Electronic Devices Work?
Table of Contents
ToggleElectronic devices—and by extension, electron devices and circuits—constitute the essential building blocks of any electronic system. These electronic devices range from passive components such as resistors and capacitors to active components like transistors and integrated circuits that shape functionality in modern products. Understanding the electronic device definition empowers OEM engineers and procurement teams to make informed decisions surrounding design and sourcing.
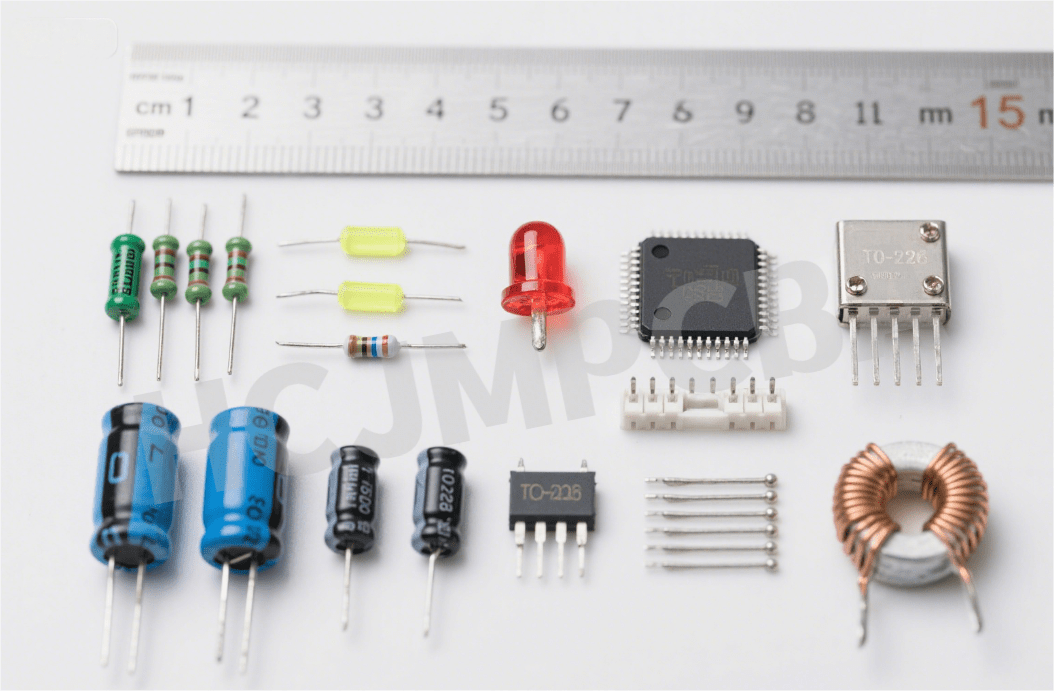
-Electronic device definition: Fundamental units such as resistors, capacitors, transistors, and sensors used in circuits.
-Related expressions: devices define, define electronics, electronic devices meaning, all emphasizing the tangible components within a circuit.
Passive components (resistors, capacitors, inductors): Do not amplify or require power to control signals.
Active components (transistors, diodes, ICs): Power-dependent components that can amplify, switch, or process signals.
ICs are compact assemblies containing transistors, resistors, capacitors—and sometimes entire functions—etched onto semiconductor chips.
Input Stage: Power or signal enters the circuit.
Processing Stage: Active and passive components manipulate signals—filtering, amplifying, or switching.
Output Stage: Resulting actions—like lighting, data output, or motion—are triggered.
Control/Feedback: Many systems use sensors or logic circuits for real-time adjustments, enhancing performance and reliability.
Electronic circuits, with at least one active component, differentiate themselves from simple electrical circuits and are essential for enabling features in modern electronics.
Everyday devices: Mobile chargers, torches, amplifiers, light dimmers—all examples of basic electronic circuits.
Underlying elements: Resistors, capacitors, LEDs, transistors, and ICs—common building blocks in consumer and industrial electronics.
Accurate component selection (e.g., choosing an appropriate resistor or IC) directly influences assembly efficiency and product performance.
Knowledge of electronic devices types and electronics and devices supports optimized BOM development and smoother manufacturing.
It enables cost-effective decision-making while safeguarding product reliability and manufacturability.
Consider these four professional criteria:
Component expertise: Can the supplier handle both passive and active components with precision?
Circuit fabrication capabilities: Does the supplier support complex layouts, dense placement, and multilayer PCB assembly?
Quality control measures: Look for AOI, ICT, and IPC-standard testing protocols.
DFM support: Can they optimize circuit design for efficiency, cost, and yield?
HCJMPCBA excels across these domains, ensuring reliability in the electron devices and circuits integrated into each PCB assembly.
Q:What exactly defines an electronic device?
A:Electronic devices are components—like resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, or ICs—that manipulate or control electric signals within a circuit.
Q:How do electronic circuits differ from electrical circuits?
A:Electronic circuits always include at least one active component (transistors or ICs), enabling signal modification and data processing, whereas electrical circuits may simply conduct electricity without control or amplification.
Q:What types of electronic devices should a PCBA engineer be familiar with?
A:Passive components (resistors, capacitors, inductors), active components (transistors, diodes, ICs), and integrated form factors that combine multiple functionalities into compact solutions.
Electronic devices are the cornerstone of modern electron devices and circuits, enabling everything from signal processing to control systems in advanced applications. Understanding how these components work—and how to choose the right ones—is essential for dependable PCBA sourcing and manufacturing.
To learn more about PCBA services, please contact Guangzhou Huachuang Precision Technology.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of PCB and PCBA, their significance, manufacturing pr
Understanding the difference between active and passive components is foundational for reliable PCBA
Discover what a 10k resistor is, how to read its color bands, and why this fundamental component is