ISO 13485-Certified PCBA Processing: How Guangzhou Huachuang Precision Ensures High-Reliability for Medical, AI, and Industrial Electronics
Guangzhou Huachuang Precision Technology Co., Ltd. excels in PCBA processing. It starts with order a
10 Compelling Reasons Why Discharging Capacitors Is Non-Negotiable + Expert’s Step-by-Step Guide on How to Discharge a Capacitor Safely
Table of Contents
ToggleCapacitors — whether in power supplies, signal filters, or motor drives — store electrical energy even after the main power is switched off. This residual charge can persist for minutes or longer, presenting silent hazards if improperly handled. In PCBA environments where engineers and technicians work close to live circuits, understanding why discharging capacitors is vital and how to discharge a capacitor safely can mean the difference between routine maintenance and serious injury.
Capacitor incidents have caused severe shocks and sparks when technicians assumed circuits were safe. Although rare, such incidents illustrate why discharge procedures are essential before testing or touching board components.
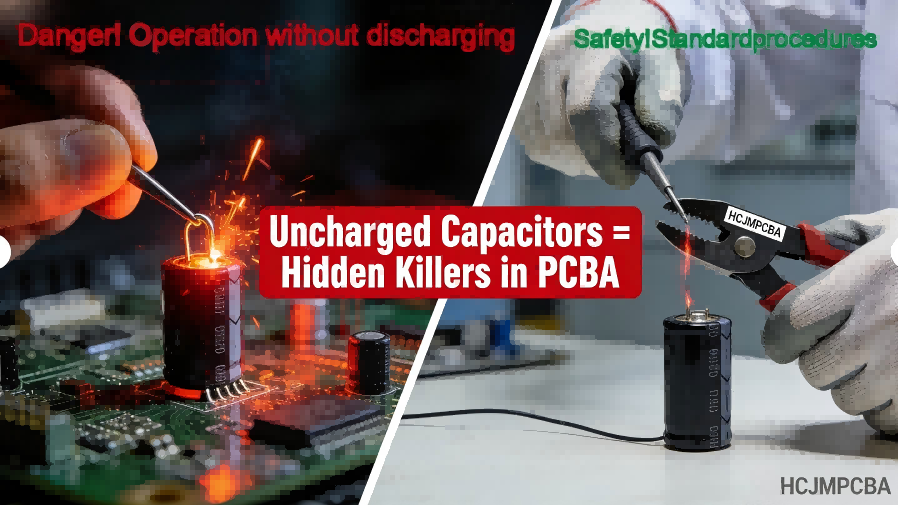
Warning Comparison Banner Image
A capacitor charged to hundreds of volts, such as a 450V filter capacitor in a power supply, can deliver a painful or potentially fatal shock if touched. This is because stored energy — even in the absence of mains power — can arc across gaps or through a technician’s body.
If a capacitor isn’t discharged before repair or testing, it can unintentionally discharge through sensitive test equipment such as multimeters or oscilloscopes, leading to instrument failure and costly repairs.
International assembly and safety standards (e.g., IPC-A-610) emphasize that circuits must be de-energized — including discharged capacitors — before in-circuit testing or rework, to protect both personnel and devices.
An undischarged capacitor-induced failure can halt production lines, necessitate rework, or even result in injury liability. Investing time in safe discharge procedures upfront protects throughput and brand reputation.
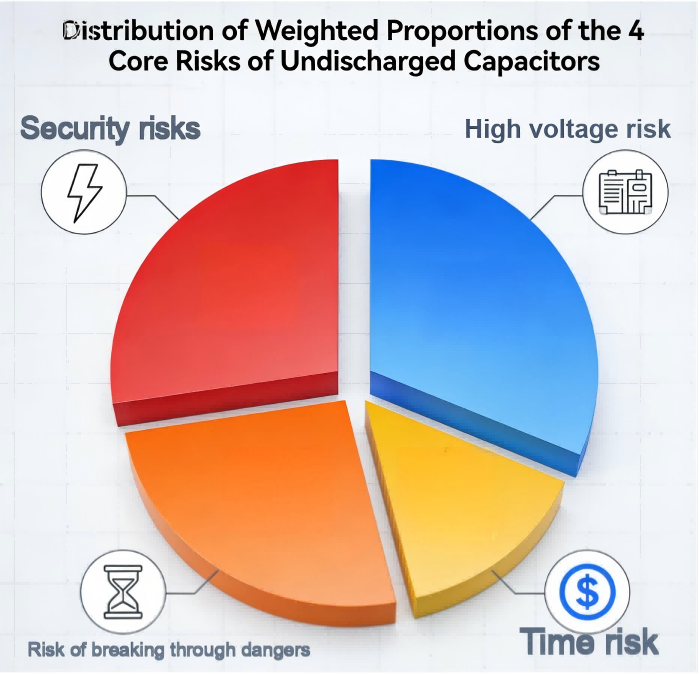
Distribution Of Weighted Proportions Of The 4 Core Risks Of Undischarged Capacitors
Capacitors store charge by holding opposite electric charges on two plates separated by an insulator. When you discharge a capacitor, that stored charge is released through a safe path, typically a resistor or purpose-built discharge tool, allowing the voltage to drop gradually.
Most circuit designs rely on internal bleed resistors to slowly discharge capacitors after power removal. However, these resistors often aren’t sufficient for immediate safety. Capacitors can retain dangerous charge long after devices are unplugged.
Capacitance value and voltage rating directly influence how much energy a capacitor holds — larger capacitance and higher voltage mean more energy stored. When discharging, this energy must be dissipated safely to avoid sparks and damage.
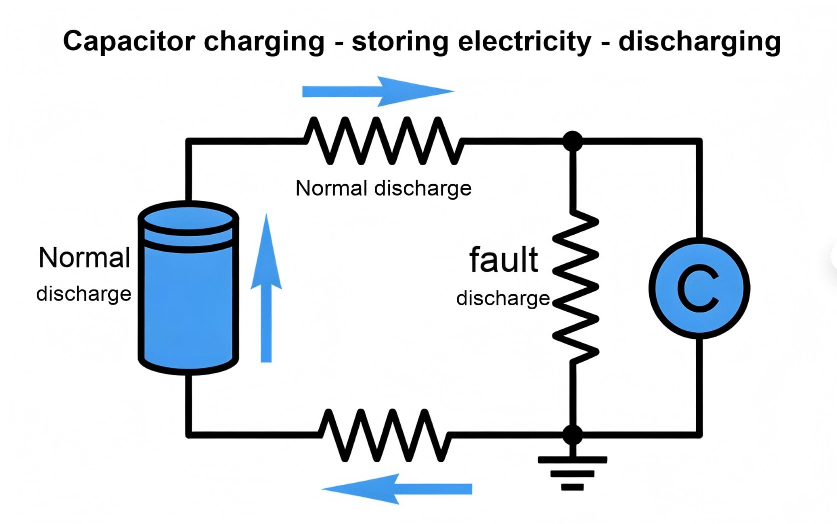
Schematic Diagram Of The Principle (21)
Before you start, gather:
Capacitor Discharge Tool: A dedicated unit with built-in resistor limits current safely.
Insulated Resistor for Discharge: Between 1 kΩ–100 kΩ with adequate power rating (2–5 W or more) depending on voltage.
Multimeter or Ohm Meter: To confirm voltage before and after discharge.
PPE: Safety glasses and insulated gloves to protect against shock or sparks.
Step 1: Power Off & Isolate the Circuit
Always disconnect primary power sources and ensure the device is unplugged.
Step 2: Identify Capacitor Type and Ratings
Read the capacitance (µF) and voltage (V) printed on the capacitor to choose appropriate discharge methods.
Step 3: Choose a Discharge Method
Resistors across terminals (recommended) provide controlled discharge, limiting current and reducing heat/sparks. Screws or metal tools are discouraged due to sparking risk, especially in high voltage contexts.
Step 4: Execute Discharge
Connect the resistor (or tool) between capacitor terminals using insulated clips. Hold for several seconds; larger capacitors take longer.
Step 5: Verify with Test Tools
Use a multimeter or ohm meter to ensure voltage is near zero before handling.
Step 6: Document and Log the Discharge
For quality control and traceability in PCBA manufacturing, record discharge procedure completion.

Complete Safe Discharge Process
AC capacitors in motors or HVAC units may store significant energy. Use a resistor method (e.g., 10 kΩ, 2 W) and insulated tools for safety.
High-voltage capacitors require careful resistor selection and extended discharge time. Never rely on internal bleed resistors alone; always verify with a multimeter after discharge.
Microwave capacitors can retain lethal charges. They often require tools specifically rated for high voltage and professional PPE before discharge.
Even lower voltage caps on PC boards (5V–50V) can damage ICs or cause zaps. The resistor method with alligator clips and multimeter verification is advisable.
A resistor limits current and allows a smooth discharge. Selecting resistor value and power rating based on the capacitor’s energy (E = 0.5 C V²) ensures controlled energy dissipation.
Without testing, you may assume a capacitor is safe when charge remains — a dangerous assumption.
Metal screwdrivers or direct shorts cause sparks and arc flash risks. Resistors are safer.
For electrolytic caps, incorrect polarity during discharge can cause internal damage or explosion.
After discharge, some capacitors regain a small voltage due to dielectric absorption — always re-test.

Error Comparison Chart
HCJMPCBA integrates discharge verification into PCBA testing workflows with multimeter, oscilloscope, and controlled discharge tools.
Advanced labs ensure accurate readings and discharge procedures, preventing residual voltage surprises.
HCJMPCBA follows IPC-A-610 and other safety protocols to guarantee safe capacitor handling across all PCBA processes.
For 450V+ applications, HCJMPCBA provides specialized tools and PPE to ensure safe discharge in demanding environments.
Decades of experience and zero safety incidents in capacitor handling demonstrate HCJMPCBA’s expertise.
Q: Can a 450V capacitor kill you?
Yes — even without mains power, stored charge in high-voltage capacitors can deliver a severe shock.
Q: How long does it take to discharge a capacitor safely?
Time depends on capacitance and resistor used — larger caps take longer and require resistors with higher power ratings.
Q: Can I use a multimeter alone to discharge?
No — a multimeter only measures voltage. You must use a discharge path before measurement.

Brand Capability Display Chart
Discharging capacitors isn’t optional — it’s a critical safety and quality step in every PCBA process. Following robust discharge methods protects personnel, equipment, and product quality. With HCJMPCBA’s structured procedures, advanced lab support, and commitment to safety, capacitor discharge becomes a reliable, documented part of your manufacturing workflow.
Learn more about PCBA services, please contact Guangzhou Huachuang Precision Technology.
Guangzhou Huachuang Precision Technology Co., Ltd. excels in PCBA processing. It starts with order a
Learn exactly how to convert watts to amps in DC, single-phase AC, and three-phase systems with clea
Learn how to discharge a capacitor safely and effectively for PCB/PCBA operations. This guide explai